This web page was produced as an assignment for Genetics 677, an undergraduate course at UW-Madison.
Small Molecules: Lithium
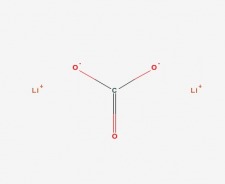
Lithium (shown above) is the most common medication given to people diagnosed with bipolar disorder. Amazingly, the mechanism of action is still unknown. Elucidation of the mechanism of lithium, especially in regards to its possible action on the glutamate receptor and its ligand binding site is a must. The active principle is the lithium ion Li+ although it is administered in a lithium carbonate form as shown above. The ion has a smaller diameter than either Na+ or K+, so in a watery environment like the cytoplasmic fluid, Li+ binds to the hydrogen atoms of water making it larger than either Na+ or K+ ions. How Li+ works in the central nervous system is still a matter of debate. Li+ elevates brain levels of tryptophan, 5-HT (serotonin), and 5-HIAA (a serotonin metabolite). The serotonin system is related to stability of mood. Li+ also reduces catecholamine activity in the brain (associated with brain activation and mania), by enhancing reuptake and reducing release. Therapeutically useful amounts of lithium (~ 0.6 to 1.2 mmol/l) are only slightly lower than toxic amounts (>1.5 mmol/l), so the blood levels of lithium must be carefully monitored during treatment to avoid toxicity. The side effects of lithium are not pleasant. Common side effects of lithium treatment include muscle tremors, twitching, ataxia. Long term use is linked to hyperparathyroidism, hypercalcemia, (bone loss), hypertension, kidney damage, nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (polyuria and polydipsia) and seizures. (2)
The paper shown above is just one example of studies that show lithium is still the most effective medication for patients with bipolar disorder. (1)
Microarray Data - ATLAS
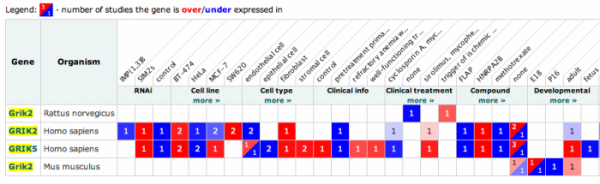
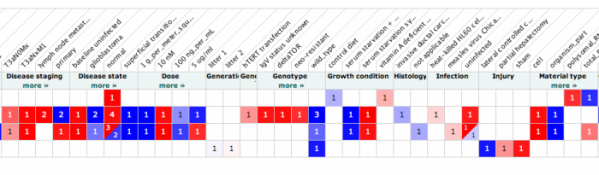
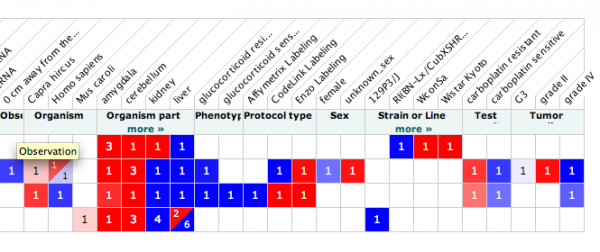
Some of the more relevant and interesting experiments involved rats with access to alcohol or cocaine, and the levels of the glutamate receptor mRNA associated with such events. in the cerebellum and amygdala, as shown in the last image.
Many of the experiments were in relation to other neuronal disorders, such as autism and Huntingtons, where GRIK2 has also been implicated.
1. Freeman, Thomas WW, Jeffrey L. Clothier, Peggy Pazzaglia, Michael D. Lesem, and Alan C. Swann. "A double-blind comparison of Valproate and Lithium in the treatment of acute mania." American Journal of Psychiatry 149 (1992): 108-11.
2. "Lithium" http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lithium#Medical_use. Accessed 5/13/09. (Image accessed here also.)
ATLAS (information and figures)
Ashley Bateman, [email protected], last updated 5/13/09
http://www.gen677.weebly.com