This web page was produced as an assignment for Genetics 677, an undergraduate course at UW-Madison.
DNA Phylogeny
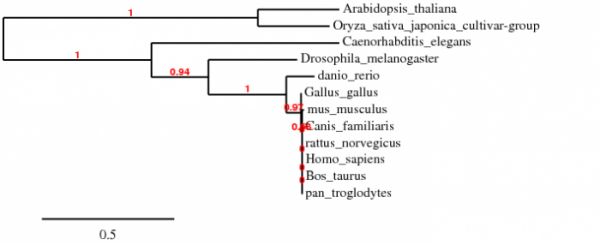
Phylogeny of species with putative homologues of GRIK2. Created using Phylogeny.fr. Phylogenies created using TreeTop and TreeFam provided the same relationships among the species.
DNA Sequence Motifs
Using MOTIF with a cutscore of 85, a total of 152 motifs were found using the mRNA transcript of variant 1 of GRIK2 as the query sequence. The highest scores were for motifs that included heat shock factors in both Drosophila and yeast, alcohol dehydrogenase gene regulator, and various transcription factors. Other transcription factors and signaling motifs were scattered throughout the sequence. No general pattern could be found that would indicate one motif being more important or more prevalent than another.
Protein Sequence

Primary protein sequence of GRIK2. Obtained from geneontology.org.
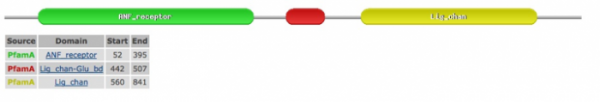
Protein Sequence Motifs
The image shown below was rendered using the SMART database. This database was chosen because it incorporates PFAM, another reliable protein database, into its results. This image was identical for every species' sequence query: Homo sapiens, Pan troglodytes, Canis lupus familiaris, Mus musculus, Bos taurus, Rattus norvegicus, Gallus gallus, Danio rerio, Drosophila melanogaster, Caenorhabditis elegans, Arabidopsis thaliana, and Oryza sativa. This highlights the highly conserved nature of the putative functional domains in GRIK2 and its homologues.
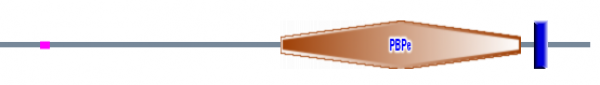
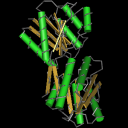
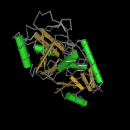
"Orange Polygon"/PBP: Bacterial periplasmic transport systems use membrane-bound complexes and substrate-bound, membrane-associated, periplasmic binding proteins (PBPs) to transport a wide variety of substrates, such as, amino acids, peptides, sugars, vitamins and inorganic ions. PBPs have two cell-membrane translocation functions: bind substrate, and interact with the membrane bound complex. A diverse group of periplasmic transport receptors for lysine/arginine/ornithine (LAO), glutamine, histidine, sulfate, phosphate, molybdate, and methanol are included in the PBPb CD. This sequence motif makes sense given the putative function of GRIK2 as a glutamate receptor (1).
"Blue Bar"/Type 1 periplasmic binding fold superfamily: The periplasmic binding proteins are the primary receptors for chemotaxis and transport of many sugar based solutes, as would be the case in a glutamate receptor. The core structures of periplasmic binding proteins are classified into two types, and they differ in number and order of beta strands: type 1 shown here has six beta strands, while type 2 has five beta strands per sub-domain. These two structural folds are thought to be distantly related via a common ancestor. The phylogeny on the previous page supports this notion of distant relatedness (2).The purple bar represents a low complexity region.
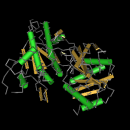
The structural images on the left side of the page below are JMOl images from the PFAM database. They are the structural illustrations of the domains discussed below.
References:
1. NCBI Database. "Conserved Domains". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/cddsrv.cgi?uid=cl00115. Retrieved February 28th, 2009.
2. NCBI Database. "Conserved Domains". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/cddsrv.cgi?uid=cl10011. Retrieved Ferbruary 28th, 2009.
SMART
PFAM
GO CONSORTIUM
PHYLOGENY.FR
Ashley Bateman, [email protected], last updated 5/13/09
http://www.gen677.weebly.com